What Is Configuration Management Database?
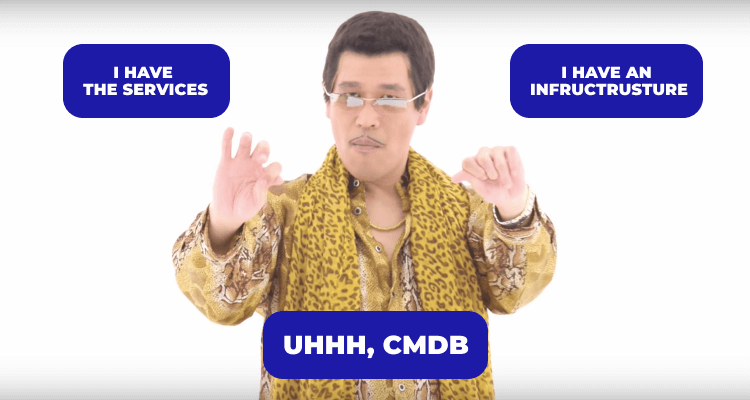
CMDB is a database that serves as a data warehouse that stores details on your IT environment, including the hardware and software needed to provide IT services. Lists of assets (also known as configuration items) and the connections between them are among the information kept in a Configuration Management Database.
Modern IT operations are centered around configuration management databases (CMDBs), which allow businesses to manage information about various IT components in one location.
The CMDB assists the organization in carrying out service management procedures like incident management, change management, and problem management. It also serves as a vital informational tool for decision-makers who require data to enhance the cost, quality, and performance of the organization’s IT services.
CMDB Characteristics
1. Integrated Dashboards 📊
It is simple to track the health of data, the impact of changes, trends that indicate incidents or difficulties and the health of the CIs, thanks to the integration of dashboards with CI metrics and analytics. It dramatically shortens the time it takes to resolve a problem by providing the operations team with real-time insights about the preceding incident, problem, and change associated with a CI.
2. Access Limitations 🚧
Access controls allow the flexibility to assign multiple access levels to people or teams as needed and track any changes back to their original location in case of an incident or query.
3. Compliance 📝
You will receive thorough records for the purpose of visibility and auditing. The condition of CIs, historical changes, checks and balances, and occurrences are among the insights into records.
4. Data Population and CI Creation ⚙️
This is backed by three distinct approaches that all search IP addresses within a company’s network to identify software and hardware information: integrations, discovery tools, and manual input. A company’s entire inventory of resources, including cloud resources, is created through this procedure.
5. Combined Data Sets 🗄️
Assistance with federated data sets includes CI normalization and reconciliation of the necessary data.
6. Service Mapping for IT 📍
A tangible illustration of the connections and interdependencies relating to an IT service.
How Does a CMDB Function?
A Configuration Management Database is a repository (a database) that houses relationships and lists of data. The data that a CMDB includes is what distinguishes and adds value to it.
The physical IT environment’s connective tissue is described by lists of configuration elements, their corresponding attributes, and the relationships between them. The CMDB is frequently included in a larger IT Service Management (ITSM) platform or suite of capabilities, which will probably also include tools for discovering and importing data into the CMDB and tools for consuming data from the CMDB. The CMDB functions by offering a central location where employees can access data on IT assets and other configuration elements. Without the CMDB, it would be exceedingly challenging to put together a complete and accurate picture of the IT environment because this data is frequently gathered from various sources.
Most of the time, configuration elements in the IT environment are found and added to the CMDB using discovery and data import technologies. Some businesses may manually update their CMDB data through audits and inventories.
The information can then be accessible by tools and processes that need to consume it in a uniform, and consistent manner after data from the various sources has been loaded in the CMDB.
Due to the volume of data present and the format in which it is kept, accessing configuration data straight from the CMDB is uncommon. Rows and columns of data are challenging to interpret. Other ITSM tools and reporting capabilities play a part in this.
These tools gain access to the data stored in the CMDB then sort, filter, and display it to users in a more appropriate way for the operational or business issue they are attempting to address.
Development of CMDBs
A collection of procedures for service asset and configuration management are described in the IT Infrastructure Library (ITIL), to store data on configuration items (Cis), which are the parts needed to deliver an IT service.
In addition to the lists of objects, relationships between them are also tracked as part of ITIL service asset and configuration management. The configuration management system (CMS) used by ITIL to enable asset and configuration management is represented as a logical data model that may span numerous physical CMDBs.
The CMDB plays a bigger part in helping IT staff members comprehend the production environment and make real-time choices about problems and modifications when businesses adopt new methodologies like Agile and DevOps.
Companies will need to incorporate additional external data sources into the CMDB in order to retain the overall perspective of a modern hybrid IT environment as cloud infrastructure and SaaS usage proliferate. Many firms are looking into novel approaches to managing data assets within the context of the CMDB to support digital transformation initiatives and business processes.
The CMDB will have a bigger role in future business operations and IT operations (in a digitally transformed corporation). It will be crucial to start with the correct CMDB solution, one that not only meets your demands today but also allows you to expand with your organization as the market changes.
What Advantages Does the CMDB Offer?
One of the main advantages of CMDB is that it consolidates all the siloed data needed to run IT across the enterprise into one location, allowing IT operations visibility into all the IT resources in the company. It stops data from being dispersed among numerous sites.

Here are just a few ways a CMDB benefits IT teams: it helps prevent outages, drastically shortens the time it takes to fix an outage, maintains compliance, prevents security and audit fines, helps decision-makers understand key service contexts, which improves risk assessment and reporting and tracks software license and cloud costs.
Planning
CMDB aids technology managers in making plans for both high-level enterprise architecture and detailed asset management.
Accounting
Applications and service codes are crucial for IT finance since they facilitate the distribution of billing statements and the management of other finances.
Operating
CMDB enhances fundamental ITSM techniques, including incident, change, and problem management. By anticipating which systems and users may be most negatively affected, CMDB helps enhance risk assessment in change management. Assisting teams in managing audit trails and controls, also promotes compliance.
By locating the modifications and underlying reasons for an issue and working toward a quicker resolution, CMDB impacts incident management. Teams can follow incidents over time together with the assets affected by the occurrence because incident records are linked to their CIs.
CMDB enhances problem management by assisting with root-cause analysis, which enables teams to locate a problem’s origin more rapidly. Additionally, it helps teams discover assets that require an upgrade to cut down on service costs and downtime. This enables proactive management.
Why Is It Essential to Have a Configuration Management Database?
An organization needs the configuration management database because IT infrastructure is becoming more sophisticated and is a key part of the ITIL framework. Additionally, as your IT infrastructure becomes more complicated, monitoring and comprehending the information in your IT environment also becomes more crucial.

For IT leaders who need to identify and validate each element of their infrastructure in order to manage and enhance it, using a CMDB effectively is regarded as the best practice. Other advantages of using one of these for CMDB include:
- Increased awareness of users and connected CIs.
- Efficiency gains from a single source of information on the IT system.
- Improved decision-making with precise, current facts.
- Reduced downtime due to the problem, incident, and event mitigation.
- Automation lowers the expenses of operations, equipment, and labor.
- Faster MTTR because it can perform root-cause analysis and comprehend CI connections.
- Reduced risk through enhanced change management.
Problems with CMDB
Despite the clear benefits of CMDB, many organizations struggle to reap the benefits of their CMDB solutions.
Here are just a few reasons why: manual processes were used to build the CMDB, there were no established procedures or methods for identifying the crucial data that needed to be transferred into the CMDB, and there were no automated tools to make sure the data was placed in the correct location in the CMDB.
However, this does not imply that the technology is inherently defective; problems that can impair CMDB effectiveness can be anticipated and avoided by figuring out the variables involved.
Accuracy 🏹
Maintaining the accuracy of a CMDB can be challenging; some of these challenges include discovery tools not being used frequently enough, a lack of automated protocols, or an excessive reliance on data input. Accuracy will increase due to concentrating on and optimizing discovery within your CMDB.
Centralization 🎯
Although a CMDB is a centralized location to examine data, not all asset data must necessarily reside there. A great practice is using information from different tools such that the one most pertinent to each instance is used to support it.
Several Sources of Data ☁️
A CMDB serves as a central store for data about IT assets. However, there may occasionally be too much data coming from sources that are feeding the CMDB. This could make it harder to categorize the data and cause confusion.
Process ➡️
Some businesses operate under the misconception that CMDBs are used to map outdated systems rather than the new cloud and software infrastructure stack. It’s crucial to avoid letting the debate over semantics stop you from tracking the value of your CIs in a platform that offers a comprehensive perspective of your technological ecosystems.
Relevancy 🔗
Some businesses view their CMDBs as the only reliable source of information, which might cause them to want to consolidate all of their data there without taking use cases or their specific needs into account. Only pertinent and valuable data that supports processes should be included in a CMDB; make sure to identify the value, objective, owner and methods for updating each piece of data.
Team Dedication 🤝
One of the key determinants of the effective adoption and integration of new technology and processes is the level of team commitment. Your CMDB solution is unlikely to be successful if your company and the individuals involved are not totally dedicated to its success.
Tools ⚒️
If you want to succeed, it’s essential to select the appropriate tool. Some CMDB technologies are little more than fixed asset repositories that rely on antiquated infrastructure discovery methods and have a sluggish response to change. The finest CMDB tools are ones that can swiftly adapt and that take new asset kinds into consideration.
CMDBs vs. Asset Management
For change management, there is some functional overlap between CMDBs and ITAM platforms, and these platforms’ capabilities are being more thoroughly incorporated into larger service management frameworks. They serve various functions but they are distinct tools.
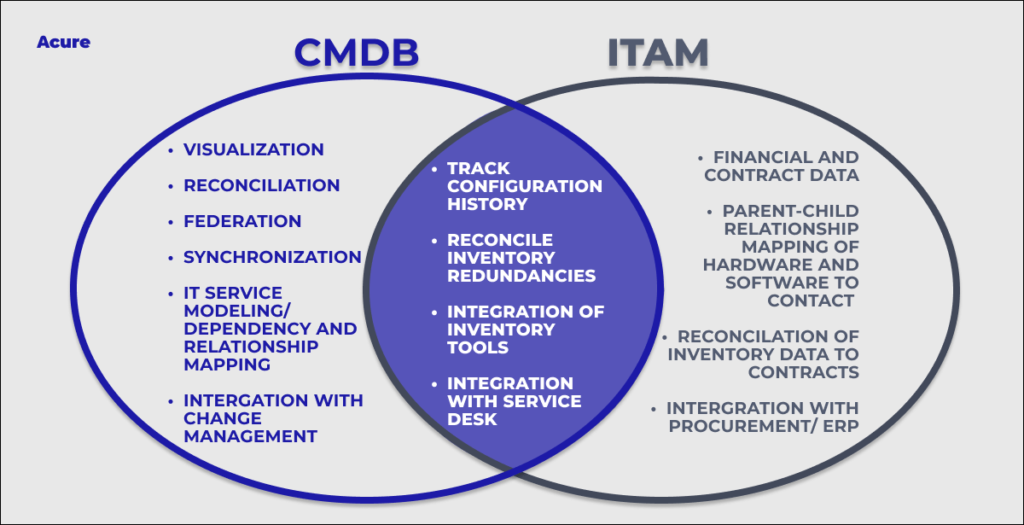
Unlike what a CMDB tracks, which includes acquisition/procurement, operation, maintenance, and disposal, an ITAM tool tracks hardware and software details throughout the whole asset lifecycle. This includes details about its configuration as well as the costs associated with each stage, such as those associated with purchasing, licensing, service/support and depreciation.
Better asset utilization and proactive asset compliance and security auditing are two advantages of asset management. Additionally, better asset visibility facilitates quicker and more precise corporate decision-making.
ITAM tools are often used to accomplish business-oriented objectives, like reviewing and making choices throughout the lifecycle of an infrastructure asset. Configuration management solutions can assist IT employees in comprehending dependencies and planning and maintaining IT services when used for service-oriented objectives.
It should be noted that CMDB and ITAM are not exclusive. An example of an IT asset is an application server. It has a cost that depreciates over time, needs upkeep, and might incorporate operational data like service agreements that are not contained in a CMDB. That server is also a configuration item, and details about it, including the installed OS and applications, the server configuration, and firmware versions, may be monitored and managed through a CMDB.
Impact analysis uses the CMDB to show the potential effects of configuration changes on performance, stability issues and security.
CMDB in Acure
In Acure, a unified CMDB is used to record CI attributes and relationships between CIs throughout their lifecycle. Using the low-code engine scenarios you can automatically build CMDB with all connections, discover the integration items and place them on automatic monitoring.
All data collected from CMDB are presented in a form of a logical service model that describes the composition and relationships of a set of configuration items that together provide the service at an agreed level. In Acure, it is a network graph containing information about model entities and their relationships.
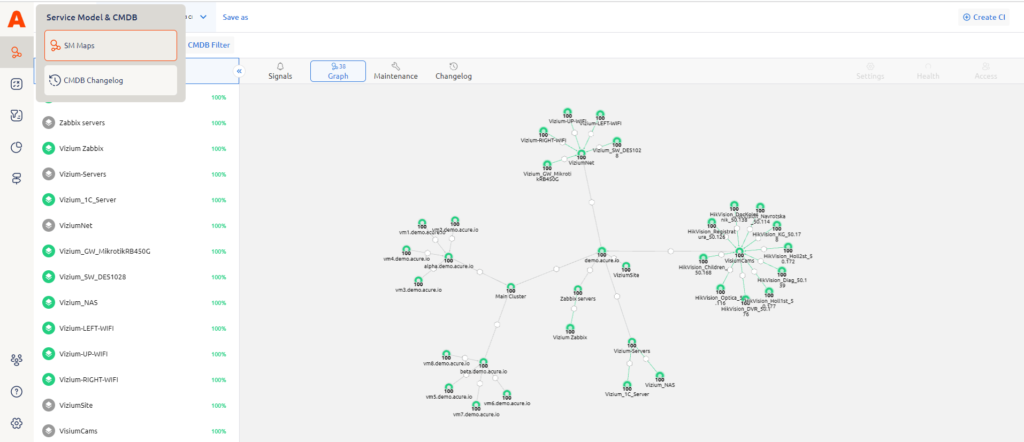
💡 Find more about a CMDB and Service Model in our documentation and try it by yourself in Userspace.
So in summation
The foundation of ITIL processes is a Configuration Management Database (CMDB). A database of data about all the parts of an information system and the configuration items (CI) in the IT infrastructure are included in the CMDB.
Hardware, software, people and documentation can all be CIs. In terms of IT asset management, a CMDB is a thorough “map” of your complete IT infrastructure that enables you to keep track of the condition of endpoint hardware, software, and data to detect and respond to security incidents.





