What Is DevOps?
Before we start talking about current DevOps trends…
DevOps is the combination of software developers (dev) and operations (ops). Its purpose is to improve the efficiency, speed, security of software development, product delivery and IT services in the context of complex applications.
🔥 Read our blog post: Top 15 Skills for DevOps

A common goal of DevOps is to transcend traditional IT operating models. An effective DevOps implementation can improve the customer experience, product quality, and agility of customer interactions.
DevOps aims at building real-time business value in a continuous-delivery environment through automation and continuous integration tools.
According to a recent market study DevOps industry will reach $20 billion by 2026, and will expand at a CAGR of 24.7% from 2019 to 2026.
The holistic approach that DevOps necessitates, which includes system thinking and the building of a positive culture, can change how traditional software development methods are done. Modern DevOps trends emphasize utilizing design systems to speed up value development.
DevOps Trends For 2022
1. Automation
The term refers to the addition of technology that performs tasks with reduced human assistance to processes such as code review, testing, and configuration management.
Automation is the utmost requirement for DevOps practice, and the guiding philosophy of DevOps is to “automate everything”.
Automation in DevOps begins with the generation of code on the developer’s machine and continues through pushing the code to the code and, even after that, monitoring the application and system in production.
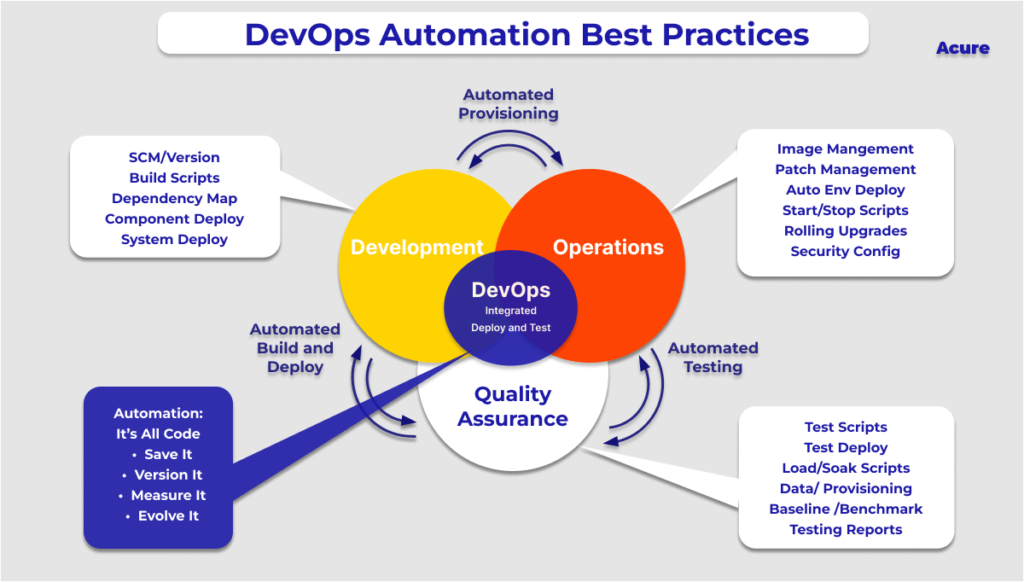
DevOps automation seeks to simplify the manual effort in the DevOps lifecycle.
According to the 2021 State of DevOps report, highly evolved companies have implemented extensive automation modes in their processes.
2. Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) And DevOps
SRE is a type of DevOps that can be applied. SRE is all about relationships and team dynamics.
To deliver services more quickly, SRE and DevOps both aim to close the gap between development and operations teams.
DevOps teams who need someone with more specialized operations expertise and whose developers are overburdened with operations responsibilities can benefit from SRE.
3. DevOps Security
DevOps security is the science and art of using strategies, policies, procedures, and technology to protect the entire DevOps ecosystem.
DevOps security should support an effective DevOps environment while assisting in the early detection and correction of operational and code issues.

Early adoption of DevOps security guarantees that security is a fundamental component of all application and system development processes. As a result, uptime is improved, the likelihood of data breaches is decreased, and strong technology is developed and made available to suit business objectives.
4. Application Performance Monitoring (APM) Software
Monitoring and controlling an application’s performance and availability are referred to as application performance management.
APM is a method that takes into account every element of a software application to comprehend it and continuously enhance it for a better user experience.
APM is now more widely available to everyone and is no longer just for the DevOps team and system administrators.
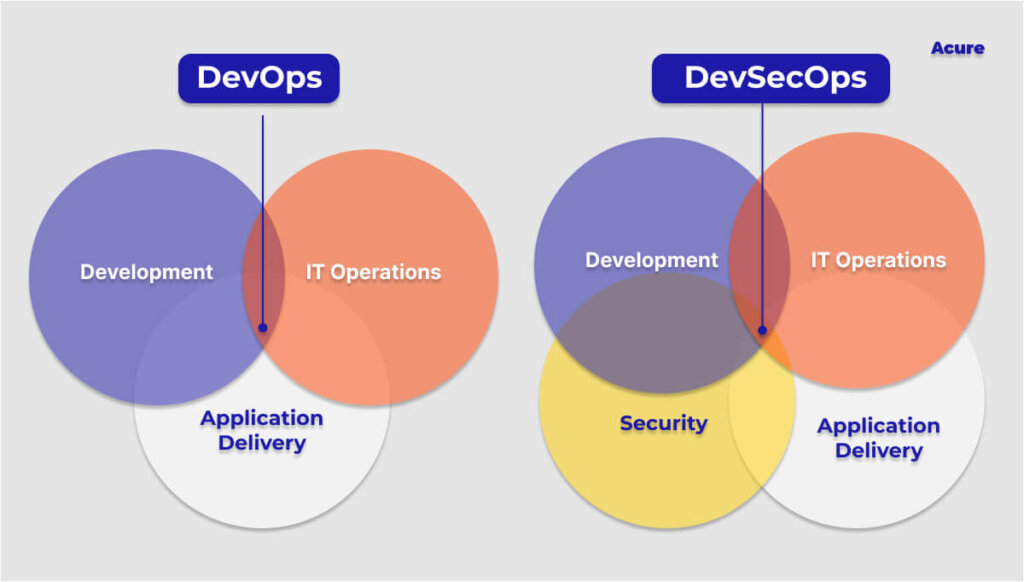
5. The Rise Of DevSecOps
DevSecOps (development, security, and operations) is the dynamic approach to software development that integrates security as a crucial step in the delivery of applications from design to production.
Automating the software delivery process with integration of security initiatives is the core of DevSecOps. It necessitates a thorough understanding of the most recent automation, AI, and machine learning techniques, as well as DevOps tools and technologies.
Businesses can automate the compliance process with the aid of DevSecOps. Replacing manual compliance processes with automated ones helps save time and resources.
6. Continued Cloud Adoption
Because of the centralized structure of the cloud and the availability of a common, centralized platform for testing, deployment, and production, DevOps and cloud computing work well together. Even while they can coexist, they work best together to deliver significant IT transformation that directly advances corporate objectives.
As cloud computing providers enable DevOps on their platforms, which is less expensive than on-premises automation technology, DevOps automation continues to become increasingly cloud-centric.
By utilizing user-based accounting to track resource usage, cloud-based DevOps facilitates the tracking of development resource expenses.
7. Autonomous IT Ops
In IT operations, the first pillar is automation. Automation is a process and it takes time to build not only the necessary skills but the necessary confidence in AI/ML technology.
The second pillar is proactive, where an operator can manually take action, but at any time in the future, automation will allow AI to fix the problem without human intervention.
Achieving full autonomy of IT operations is the democratization of AI. It’s about making relevant information available to everyone, when and where they need it, in an easy-to-use and practical way. This democratization can be achieved by simplifying AIOps platforms and making them accessible to everyone, from administrators to users.
8. AI and ML Integration
Automation of repetitive work and the elimination of inefficiencies throughout the SDLC are two ways that artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) assist DevOps teams perform better.
A significant change in its evolution will result from the combination of ML and AI with DevOps. It establishes DevOps as a critical pillar for the organization’s objective of digital transformation.
9. Kubernetes as an Evergreen DevOps Trend

Kubernetes allows organizations to leverage more computing power when running software applications. This allows the engineer to share dependencies with her IT operations.
One of the main reasons to use Kubernetes for DevOps is to reduce your workload. It also resolves conflicts between different environments. This allows engineers to meet customer demands while relying on the cloud for various work apps.
Kubernetes simplifies container tasks. It simplifies activities such as canary deployments, rolling updates, and horizontal autoscaling.
10. Observability in Application
Not only is observability critical for DevOps, but also the entire organization.
Replacing the static data of legacy monitoring solutions, observability provides a full-spectrum view of application infrastructure.
Observability helps companies monitor the performance of the application or system. It helps in speeding up the Mean Time to Detection.
Also, the management of dependencies is a crucial responsibility for DevOps managers. You may automatically map all application and infrastructure dependencies using dynamic service modeling.
***
Significant changes are being made to the key facets of DevOps. The perfect catalyst for accelerating the adoption of these DevOps trends would be the unexpected increase in the requirement for digital transformation. Although security will likely rank among the top concerns.
DevOps trends will emphasize constant advancements in several fields. No matter what the future of IT organizations holds, DevOps will continue to change and adapt. Businesses should apply these DevOps approaches to spearhead big IT transformations that directly support their goals and ambitions.

The aforementioned developments will aid firms in quickly moving past automation whileconcentrating on steadily bettering results. The establishment of a reliable release pipeline and improved communication between the business, IT, and development teams are sparked by these trends.




